专题:异步编程
蓝桥杯Web组 省赛备赛
异步编程
使用回调的异步编程
期约(
Promise)async/await
使用回调的异步编程
回调就是函数,可以传给其它函数。其它函数会在满足一定条件(或发生一定事件)后,调用这个函数。
定时器
setTimeout:
const ding = () => console.log('dong');
setTimeout(ding, 1000);setInterval:
const beep = () => console.log('beep');
setInterval(beep, 1000);const beep = () => console.log('beep');
let intervalId = setInterval(beep, 1000);let count = 0;
const beep = () => {
count++;
console.log('beep');
if (count === 3) clearInterval(intervalId);
}
let intervalId = setInterval(beep, 1000);定时器
注意:setTimeout不是真正的等待时间,而是只是一个几秒后执行任务的回调钩子。
事件
客户端JavaScript几乎全都是事件驱动的。等待用户做一些事,然后响应用户的动作。
事件监听器是通过addEventListener来添加的。
let okey = document.querySelector('#okey');
okey.addEventListener('click', () => {
console.log('clicked');
});思考:如何绑定一个事件?
<button>Click me</button><button onclick="handleClick()">Click me</button> <!-- 原生JavaScript --><button @click="handleClick">Click me</button> <!-- Vue -->defineEmits
https://vuejs.org/guide/components/events.html
思考:Vue3中如何声明一个组件将发出的事件?
<!-- MyComponent -->
<button @click="handleClick">Click Me</button> <!-- 事件将在组件内部被处理 --><!-- MyComponent -->
<button @click="$emit('someEvent')">Click Me</button> <!-- 事件将传递给父组件 --><!-- MyComponent -->
<button @click="$emit('someEvent', 1, 2, 3)">Click Me</button> <!-- 传递参数 -->在setup函数中声明事件:
export default {
emits: ['inFocus', 'submit'],
setup(props, ctx) {
ctx.emit('submit')
}
}export default {
emits: ['inFocus', 'submit'],
setup(props, { emit }) {
emit('submit')
}
}在<script setup>中声明事件:
<script setup>
defineEmits(['inFocus', 'submit'])
</script><script setup>
const emit = defineEmits(['inFocus', 'submit'])
const buttonClick = () => { emit('submit') }
</script>const emit = defineEmits<{
inFocus: [id: number]
submit: [value: string]
}>()调用事件处理程序
ele.addEventListener('click', (event) => {
console.log(event.target);
})
ele.addEventListener('click', function() {
console.log(this);
})Node.js中的回调
fs模块
const fs = require("fs"); // "fs"模块有文件系统相关的API
let options = {
// 保存程序选项的对象
// 默认选项可以写在这里
};
// 读取配置文件,然后调用回调函数
fs.readFile("config.json", "utf-8", (err, text) => {
if (err) {
// 如果有错误,显示一条警告消息,但仍然继续
console.warn("Could not read config file:", err);
} else {
// 否则,解析文件内容并赋值给选项对象
Object.assign(options, JSON.parse(text));
}
startProgram(options);
});https模块
const https = require("https");
function getText(url, callback) {
request = https.get(url);
request.on("response", response => { // 处理 "response" 事件
// 此时收到了响应头
let httpStatus = response.statusCode;
// 此时并没有收到 HTTP 响应体,因此还要再注册几个事件处理程序,以便收到响应体时被调用
response.setEncoding("utf-8");
let body = "";
response.on("data", chunk => { body += chunk; }); // 每个响应体块就绪时
response.on("end", () => { // 响应完成时
if (httpStatus === 200) {
callback(null, body); // 把响应体传给回调
} else {
callback(httpStatus, null); // 否则传递错误
}
});
});
}思考:这个复杂的代码里一共有几个回调😂?
期约(Promise)
期约是一个对象,表示异步操作的结果。
期约有一个最重要的优点,就是以线性then方法调用链的形式表达一系列异步的操作,而不用把每个操作嵌套在前一个操作的回调内部。
使用Fetch API
fetch("/api/user/profile").then(response => { // response: Response
response.json().then(profile => { // profile: JSON object
data.value = profile; // 在Vue3的onMounted钩子里更新数据
})
})fetch("/api/user/profile")
.then(response => {
return response.json();
})
.then(profile => {
data.value = profile;
})fetch(url)
.then(callback1)
.then(callback2)fetch(url)
.then(callback1, onError1)
.then(callback2, onError2)fetch(url)
.then(callback1, onError1)
.then(callback2, onError2)
.then(callback3)
.catch(error => { console.error(error); }) // 用于处理Promise链中的错误
.finally(() => { console.log("done"); }); // 用于收尾工作,无论错误与否均会触发使用Axios API
axios.get("/api/user/profile").then(response => { // response: AxiosResponse
data.value = response.data; // 在Vue3的onMounted钩子里更新数据
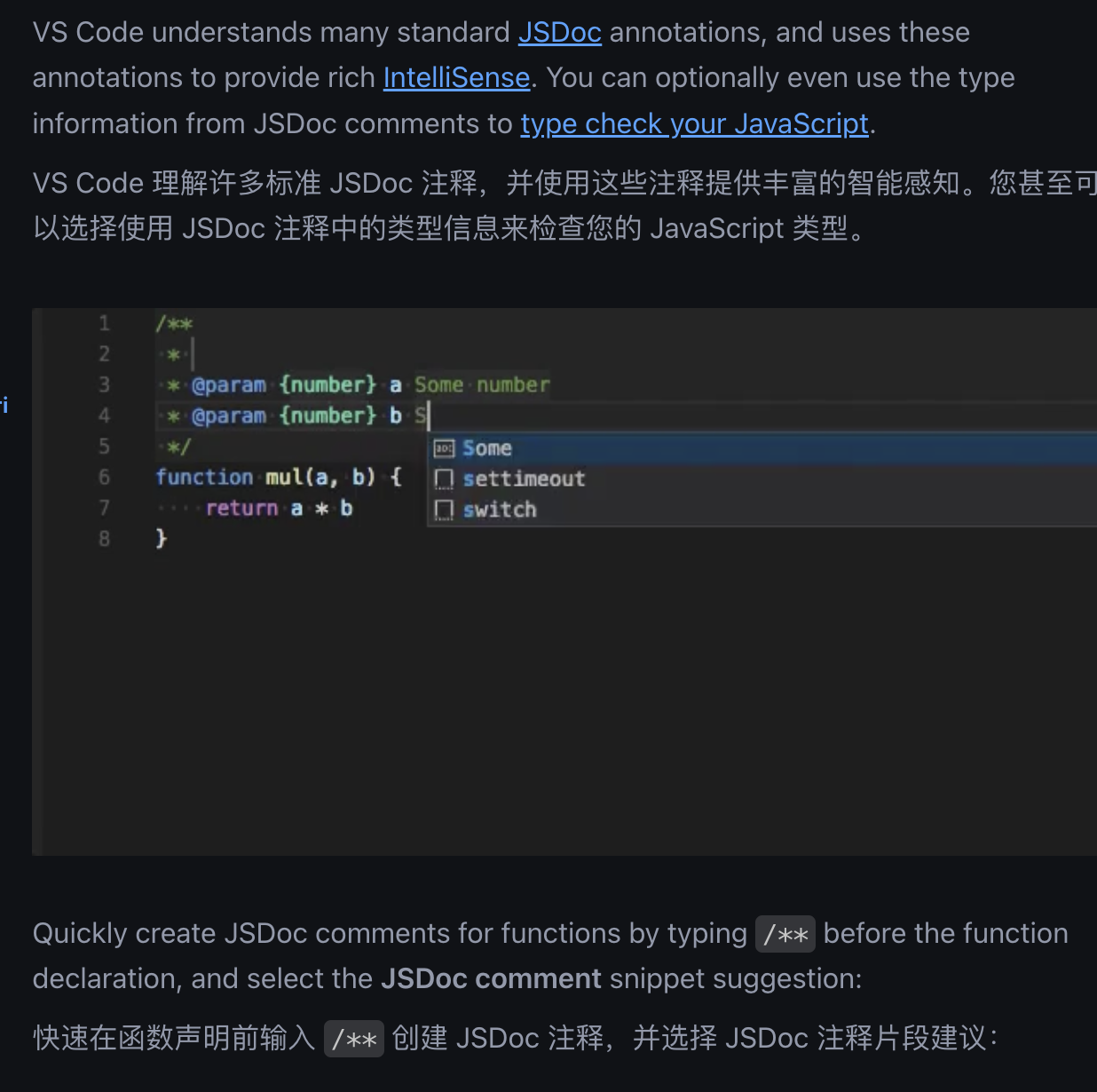
})🎉 JS Doc!
VS Code在不安装插件的情况下,原生对JS Doc提供支持。
这意味着对于很多后端开发者,或者习惯TypeScript的前端开发者来说,JavaScript不再缺少类型信息。
async和await
允许我们以同步的方式编写异步的代码。
我们发现,基于线性then的异步代码不能像正常的同步代码一样返回一个值或是抛出一个异常。
await关键字接收一个期约,将其转换成一个返回值或一个抛出的异常。
fetch("/api/user/profile")
.then(response => {
return response.json();
})
.then(profile => {
data.value = profile;
})let response = await fetch("/api/user/profile");
let profile = await response.json();
data.value = profile;📢 注意:只能在async定义的函数中使用await关键字。
把函数标注为async意味着它返回一个期约,而不是直接返回一个值。
并行期约
async function getJSON(url) {
let response = await fetch(url);
let body = await response.json();
return body;
}
let value1 = await getJSON("/api/user/profile");
let value2 = await getJSON("/api/user/friends");以上代码的问题在于它本不必顺序执行。要等候一组并发执行的async函数,可以使用Promise.all()方法。
let [value1, value2] = await Promise.all([
getJSON("/api/user/profile"),
getJSON("/api/user/friends")
]);练习:串行期约
有这样一组未知数量的url数组,为了避免网络过载,你一次只能抓取一个url,编写一个函数来构造这样的期约。
function fetchAll(urls) {
const results = [];
function fetchOne(url) {
// TODO
}
// TODO
}function fetchAll(urls) {
const results = [];
function fetchOne(url) {
return fetch(url).then(response => response.json());
}
urls.forEach(url => {
results.push(fetchOne(url));
})
return Promise.all(results);
}function fetchAll(urls) {
const results = [];
function fetchOne(url) {
return fetch(url)
.then(response => response.json())
.then(result => {
results.push(result);
})
}
let p = Promise.resolve(); // 立即兑现的期约
urls.forEach(url => {
p = p.then(() => fetchOne(url));
})
return p.then(() => results);
}练习:async/await的实现原理
async function f(x) { /* body */ }function f(x) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
try {
resolve(function(x) { /* body */ }(x));
}
catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
})
}